[SPRING] 스프링부트 JPA & DB
스프링부트 JPA & DATABASE 연동
1. JPA
작업전 H2 Database 사용 필요 > dependency 추가 필요
작업전 JPA 사용 필요 > dependency 추가 필요
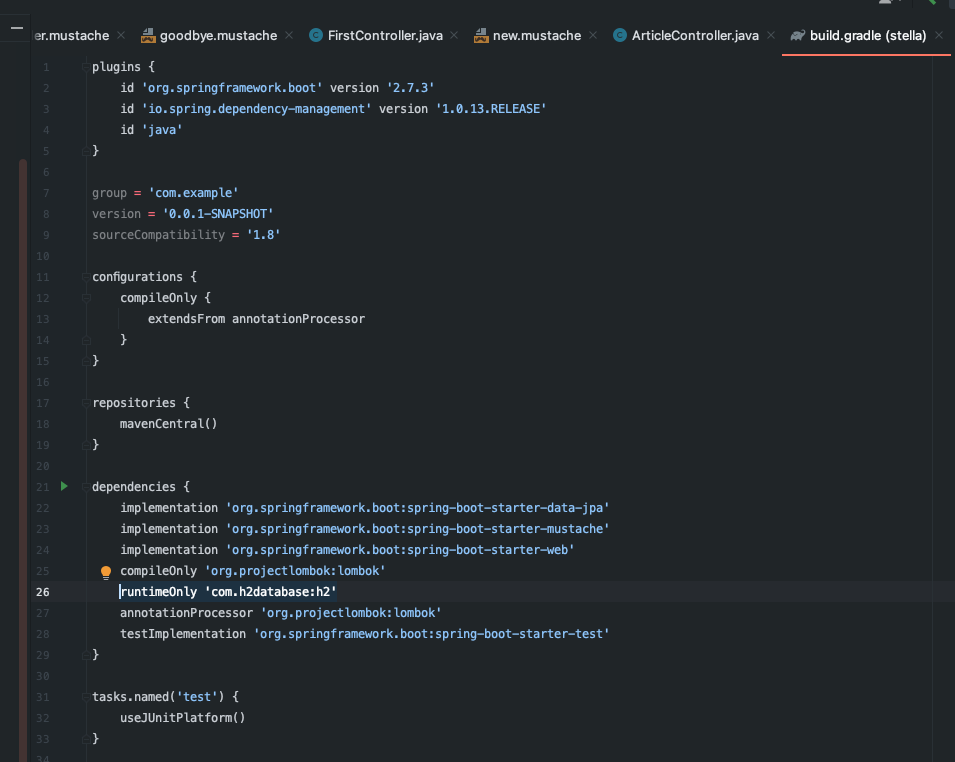
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-mustache'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
DB에 데이터를 기록하려면 어떻게 해야할까? > 문제는 DB는 자바를 이해하지 못한다.
Q. 그럼 DB에 자바를 이해할 수 있게 해주는 것이 무엇있까?!
A. 그게 이번에 학습할 JPA 이다
JPA는 데이터 관리에 필요한 여러 기능들도 제공해준다.
이러한 JPA의 핵심 도구로는 2가지가 있다.
- Entity : 자바 객체(DTO)를 DB가 잘 이해할 수 있는 규격화된 Entity로 변경
- Repository : repository라는 일꾼을 통해서 전달받은 Entity를 DB에 저장할 수 있다
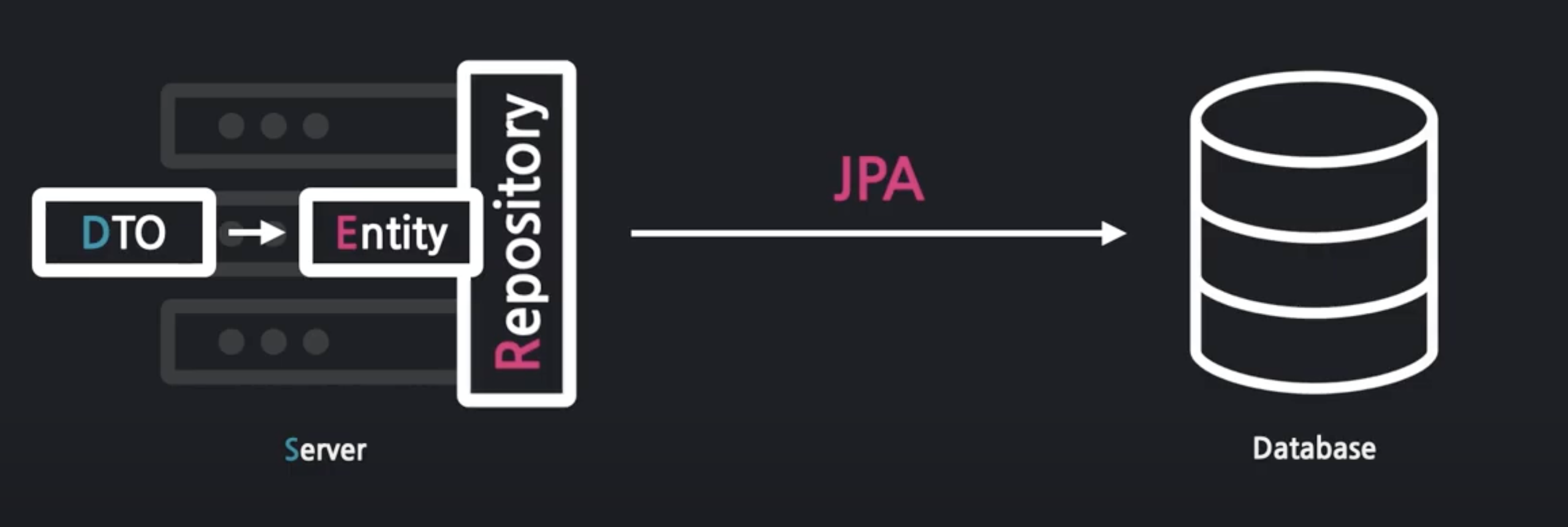
[처리흐름개요]
- DTO를 변환! Entity!
- Repository에게 Entity를 DB안에 저장하게 함
DTO를 Entity로 변환
Article article = form.toEntity()
- 먼저 form 객체는 DTO 클래스(ArticleForm)에서 만들어진 객체로 POST 방식으로 넘어올때 자동으로 생성
- [Entity] Article Entity 만들기
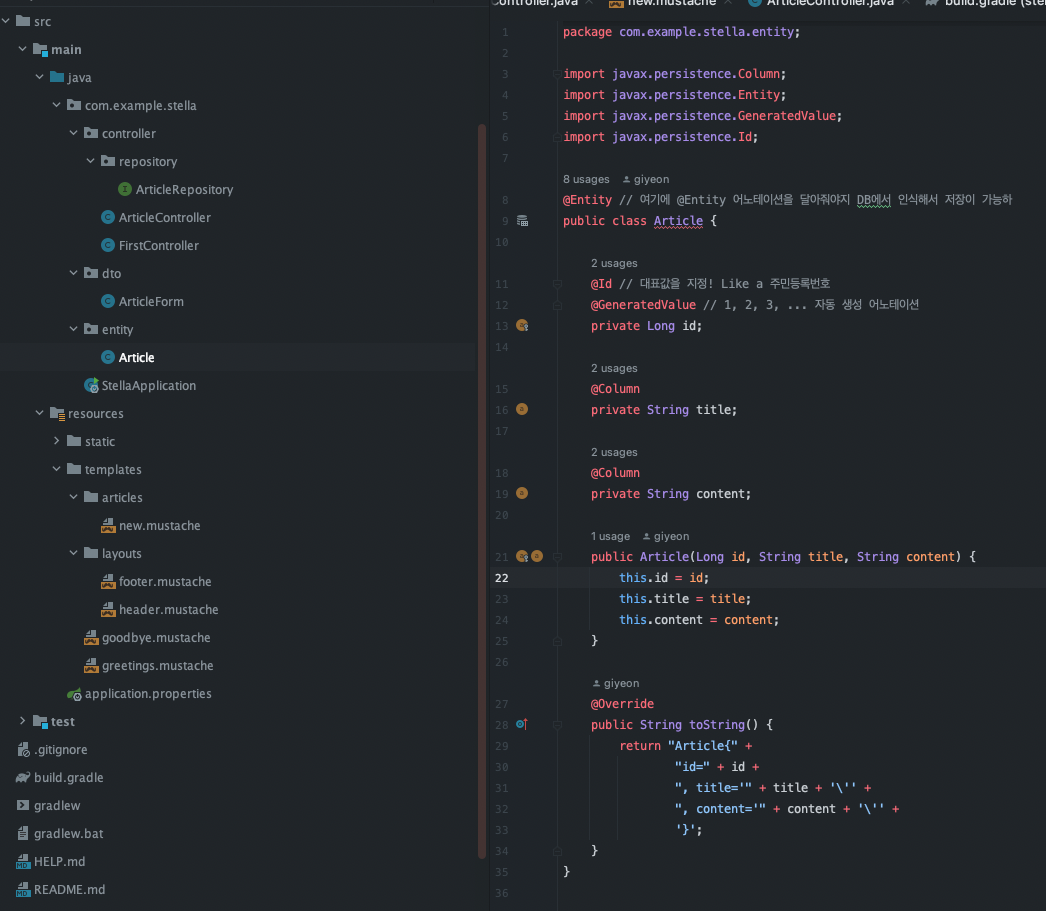
src > main > java > com.example.프로젝트 > entity > Article.java 파일 생성
** 여기서 Entity KEYPOINT **
- @Entity 어노테이션을 붙여주어야 DB에서 Entity로 인식가능
- @ID 어노테이션은 Primary Key 값을 의미한다
- @GeneratedValue 어노테이션은 자동으로 번호를 채번해주는 sequence 역할
- @Column 어노테이션은 필드값을 커럼으로 만들어주는 역할
package com.example.stella.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity // 여기에 @Entity 어노테이션을 달아줘야지 DB에서 인식해서 저장이 가능하
public class Article {
@Id // 대표값을 지정! Like a 주민등록번호
@GeneratedValue // 1, 2, 3, ... 자동 생성 어노테이션
private Long id;
@Column
private String title;
@Column
private String content;
public Article(Long id, String title, String content) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Article{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- [DTO] Article 파일에 toForm() 추가하기
package com.example.stella.dto;
import com.example.stella.entity.Article;
public class ArticleForm {
private String title;
private String content;
public ArticleForm(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ArticleForm{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Article toEntity() {
return new Article(null, title, content);
}
}
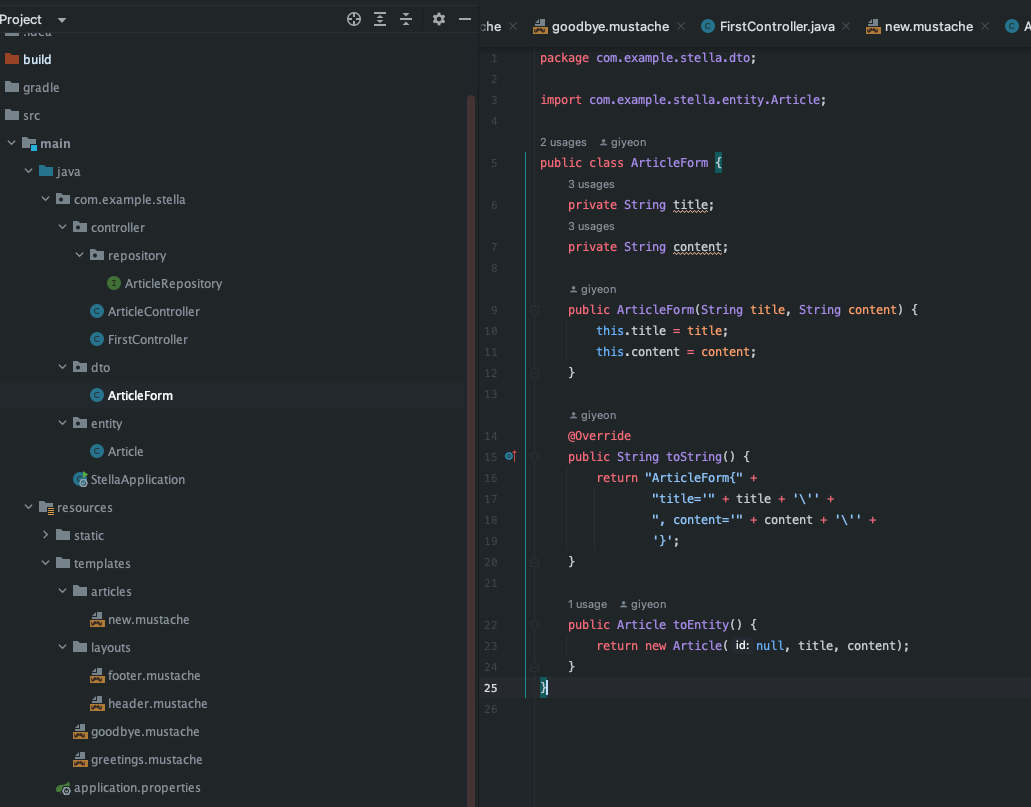
그 이후 form.toEntity()를 호출하려 하면 당연히 없기 때문에 ArticleDto 클래스에 toEntity()함수 생성
- [Repository] Repository에게 Entity를 DB안에 저장하게 하도록
단순히 이렇게 추가하면 에러 발생
public class ArticleController {
...
@Autowired //여기에 @Autowired 어노테이션으로 연결
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
...
}
Article saved = articleReoisitory.save() 수행 가능하도록 아래와 같이 만들어보자
먼저 Repository 작성
src > main > java > com.example.프로젝트 > repository 패키지 > Interface(ArticleRepository) 파일 생성
package com.example.stella.controller.repository;
public interface ArticleRepository{
}
ex) CrudRepository<Article, Long>
- Entity = Article
- PrimaryKey Type = Long id
package com.example.stella.controller.repository;
import com.example.stella.entity.Article;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface ArticleRepository extends CrudRepository<Article, Long> {
}
[궁금해서 찾아보는 CrudRepository 내부] < save, saveAll, findById … 여러 기능 포함>
이렇게 해주면 Repository 생성 완료
아래와 같이 Article saved = articleRepository.save(article) 하게 되면 정상적으로 저장하고 리턴
[최종CODE] Article Controller
package com.example.stella.controller;
import com.example.stella.controller.repository.ArticleRepository;
import com.example.stella.dto.ArticleForm;
import com.example.stella.entity.Article;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
@Controller
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired // 스프링 부트가 미리 생성해놓은 객체를가져다가 자동 연결
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
@GetMapping("/articles/new")
public String newArticleForm(){
return "articles/new";
}
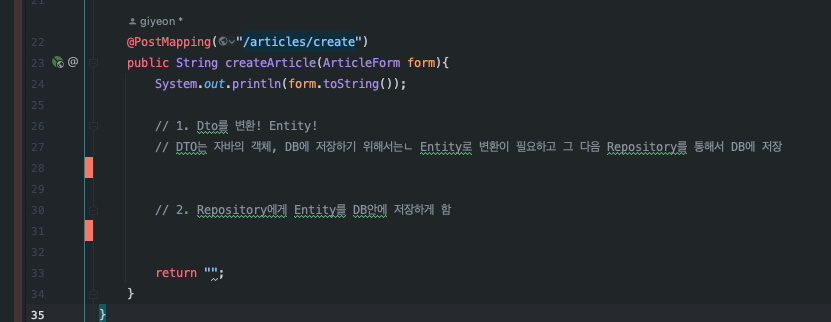
@PostMapping("/articles/create")
public String createArticle(ArticleForm form){
System.out.println(form.toString());
// 1. Dto를 변환! Entity!
// DTO는 자바의 객체, DB에 저장하기 위해서는
Entity로 변환이 필요하고 그 다음 Repository를 통해서 DB에 저장
Article article = form.toEntity();
System.out.println(article.toString());
// 2. Repository에게 Entity를 DB안에 저장하게 함
Article saved = articleRepository.save(article);
System.out.println(saved.toString());
return "";
}
}
2. DATABASE 연동
H2 Database
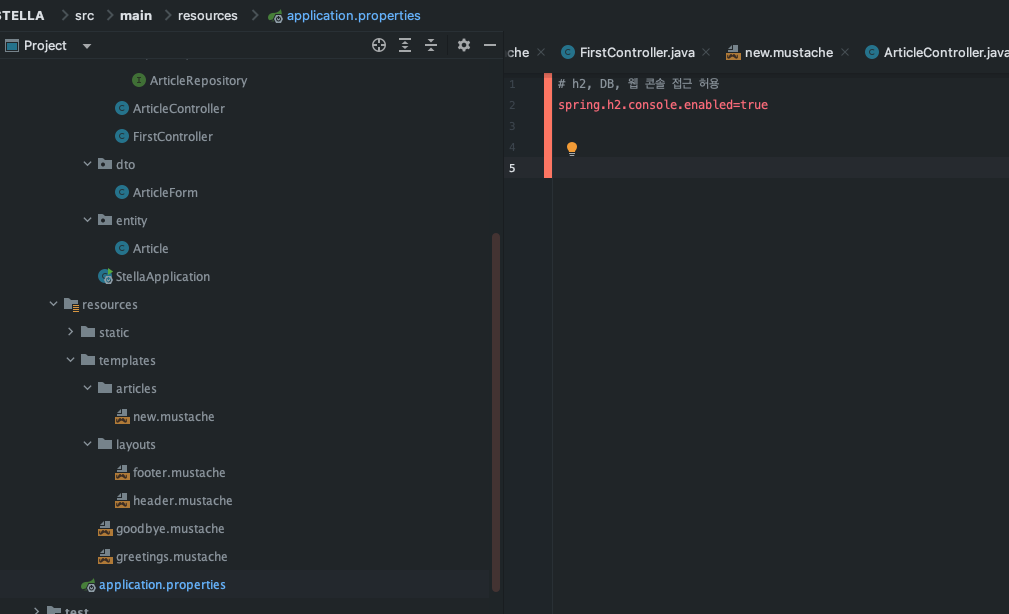
application.properties에 아래와 같이 추가해주면 WEB에서 H2 DB에 접속이 가능하다
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
WEB H2 URL 접속 방법
localhost:8080/h2-console 입력
이렇게 해주면 접속화면이 나오고 여가에서 JDBC URL을 찾아서 넣어줘야 한다.
JDBC URL은 스프링 기동할 때 아래와 같이 주소가 나오게 된다.
H2 console available at ‘/h2-console’. Database available at ‘jdbc:h2:mem:dc43092e-4034-4c14-aaf6-1d206d67fa94’
jdbc:h2:mem:dc43092e-4034-4c14-aaf6-1d206d67fa94’ //copy
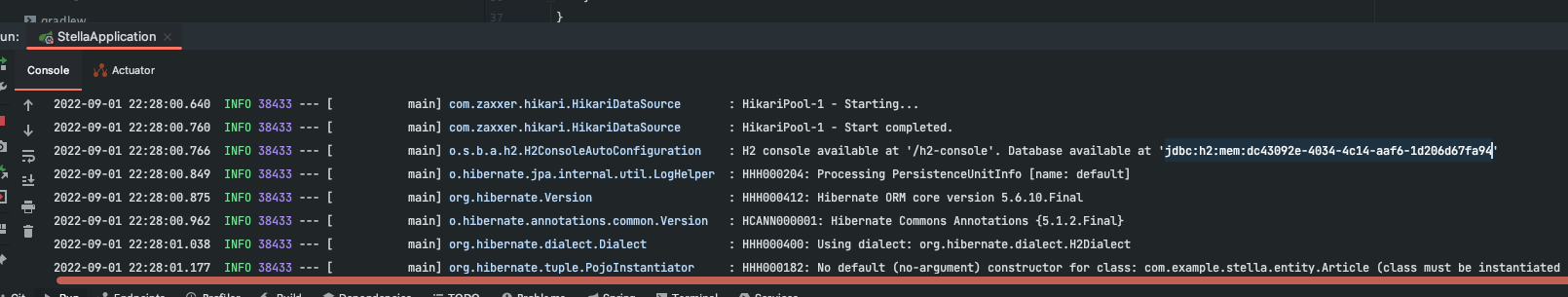
그대로 붙여 넣기
지금은 이렇게 접속하지만 나중에는 자동으로 접속하는 방법으로 접근
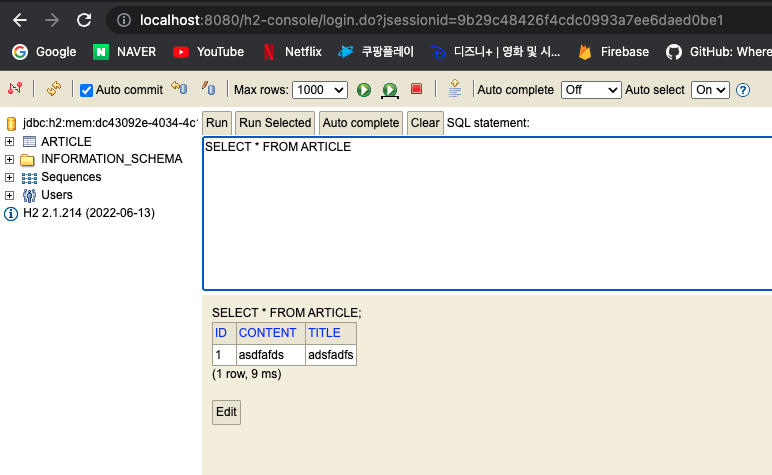
기존에 만들었던 Article Entity를 저장하게 되어 Article Table 자동 생성이 된다.
** 주의할 점 : 현재 MEM에 올려서 사용하는 DB로 해두었기에 스프링 재기동시 데이터가 모두 날라간다.
출처
댓글남기기